AddFlow Suite includes both AddFlow and LayoutFlow
Following is a list of the main AddFlow features. Note that all those features are encapsulated in a small (375 Kb only), robust, fast and easy to use ActiveX component.
General
- Runtime-royalty free
- Digitally signed
- Interactive and programmatic drawings
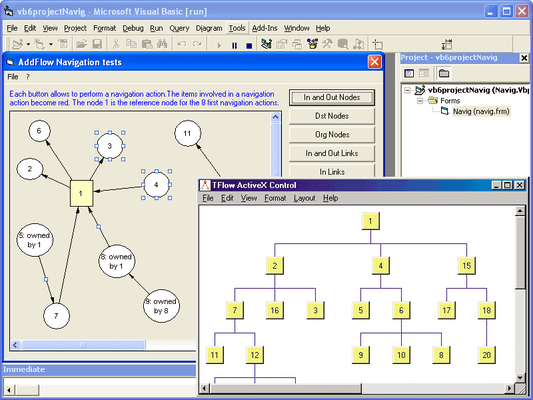
- Navigation (You can access every nodes and links of a diagram with just 5 properties)
- Collections support (nodes, links, selected nodes, selected links)
- Customization: many properties allowing to customize the control (CanDrawNode, CanMoveNode, ReadOnly, etc...)
Input/output
- Metafiles support (WMF, EMF)
- Serialisation of diagrams (LoadFile, SaveFile methods)
- XML serialisation
- Clipboard management
- Printing and print previewing
Interactivity
- Scrolling (interactive and programmatic)
- Autoscrolling
- Selection and Multiselection of nodes and links (interactive and programmatic)
- Nodes stay connected when moved or resized
Display facilities
- OwnerDraw event allowing customized drawings
- Zooming
- Grid support
Data
- Ability to associate a text, a unique key, a tooltip and a tag to a node or a link
- Nodes and links
- Change painting order of objects (ZOrder property)
- Distinct colors for each object (FillColor, ForeColor, DrawColor)
- Distinct fonts for each object
- Distinct drawing styles (DrawStyle property)
- Hidden objects
Links
- Stretchable links. A link can be composed of many segments
- Curved links (Bezier, Spline)
- Rigid links. If a link is rigid, it follows (without being stretched) its origin node when this origin node is being dragged
- Reflexive links
- Links having only vertical and horizontal segments
- Ability to adjust the position of the first and last point of a link
- 20 arrow styles for links
- Ability to customize the drawing of a link (OwnerDraw event)
- Link autorouting
Nodes
- Ability to associate a picture (bitmap, standard or enhanced metafile, icon, GIF, JPEG) to a node
- Ability to customize the drawing of a node (OwnerDraw event)
- 46 distinct shapes for nodes
- Custom shapes
- Transparent nodes
- Text alignment
- Autosize options for nodes
- Gradient color
Following is a list of the main LayoutFlow features
LayoutFlow
LayoutFlow is a set of four graph layout controls:
- HFlow (hierarchical layout)
- OFlow (orthogonal layout)
- SFlow (symmetric force directed layout)
- TFlow (tree or radial layout)
A demonstration of each of these products is available in the LayoutDemo sample provided with AddFlow.
HFlow, OFlow, SFlow and TFlow are AddFlow extensions and you cannot use them without AddFlow. Typically, you can first create your nodes and links inside AddFlow, using the AddFlow API, giving each node a random or a (0,0) position. Then you call the layout method of the graph layout control of your choice. This method will position the nodes and the links in a reasonable manner in the AddFlow control, following some aesthetic rules that depend on the chosen control (hierarchical with HFlow, symmetric with SFlow, orthogonal with OFlow...)
If the AddFlow LogicalOnly property is true, then only the logical vertices of the AddFlow control are involved in this layout. This will allow you to apply the layout only to important vertices. For instance, you will be able to exclude a node just used to display a label by setting its Logical property to false.
1) HFlow
The HFlow layout algorithm arranges vertices in horizontal layers. The orders of the vertices are chosen so that the number of crossings is kept small.
HFlow just produces a reasonable solution, not the optimum solution.
2) OFlow
The OFlow layout algorithm allows performing an orthogonal layout on a graph. The layout is orthogonal since it produces an orthogonal drawing where each edge is drawn as a polygonal chain of alternating horizontal and vertical segments.
OFlow works with any graphs, connected or not. In the resulting drawing, if the graph is a graph of maximum degree four, then each node has the same size. If the degree of a node is higher than four, then the height of the node is expanded.
3) SFlow
The SFlow layout algorithm allows performing a symmetric layout on a graph. The symmetric layout produces a high degree of symmetry and is particularly useful for undirected graphs, where the directions of the edge are not important.
The resulting layout is often good. However it requires considerable computational resources and therefore should be used for small graphs (less than 300 nodes).
Using the animation mode you can see of SFlow is working.
4) TFlow
The TFlow layout algorithm allows performing a tree layout on a graph. The tree layout applies only to a specific subset of graphs: rooted trees. In such a graph, no vertice may have more than one parent.
The drawing of the tree occupies as little space as possible while satisfying certain aesthetics. If the DrawingStyle property is "Layered":
- vertices at the same level of the tree are placed on the same line
- a parent is centered over its childs
If the DrawingStyle property is "Radial":
- the root is placed at the origin
- the layers are concentric circles centered at the origin